Stem Cell Therapy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Imagine a world where the debilitating symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) no longer dictate your daily life.
For millions struggling with the relentless cycle of pain, fatigue, and dietary restrictions, a groundbreaking treatment is offering a glimmer of hope.
Stem cell therapy, once confined to science fiction, is now emerging as a potential game-changer in the fight against IBD.
But what exactly is this innovative approach, and could it be the key to unlocking a new lease on life for those battling Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis?
Let’s embark on a journey into the cutting-edge world of regenerative medicine and discover how tiny cells are making a big impact in the lives of IBD patients.
Key Takeaways:
- Stem cell therapy is an innovative treatment option for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), offering potential relief for patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- This regenerative medicine approach uses stem cells to reduce inflammation, promote tissue repair, and modulate the immune system in the digestive tract.
- Compared to traditional treatments, stem cell therapy may offer advantages such as improved quality of life, reduced flare-ups, and decreased dependence on medications.
- Stem cell therapy for IBD typically involves intravenous infusion of high doses of stem cells, which can target and respond to injured tissue in the intestines.
- While individual results may vary, stem cell therapy shows promise for IBD patients who haven’t responded well to conventional treatments or seek to manage their condition more independently.
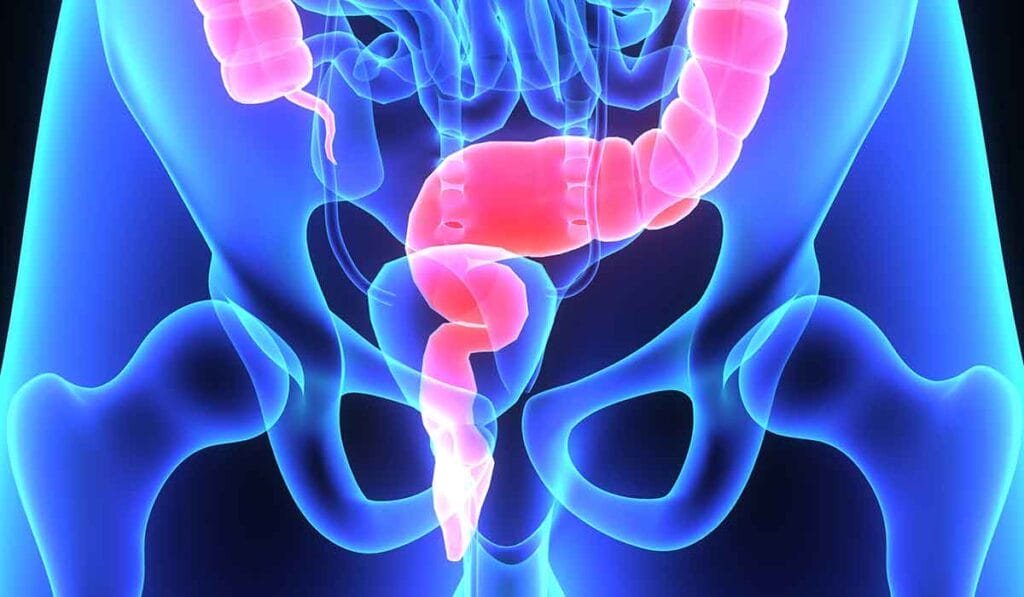
What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)?

Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of chronic conditions that cause inflammation in the digestive tract.
The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
These conditions affect over 1.6 million Americans, often diagnosed in childhood or young adulthood.
IBD can significantly impact quality of life, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss.
Traditional Treatments for IBD

Conventional treatments for IBD focus primarily on managing symptoms and reducing inflammation.
These typically include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics.
- Dietary changes: Eliminating trigger foods and following specific diets.
- Surgery: In severe cases, removal of damaged portions of the digestive tract.
While these treatments can provide relief, they often come with significant side effects and may not address the root cause of the disease.
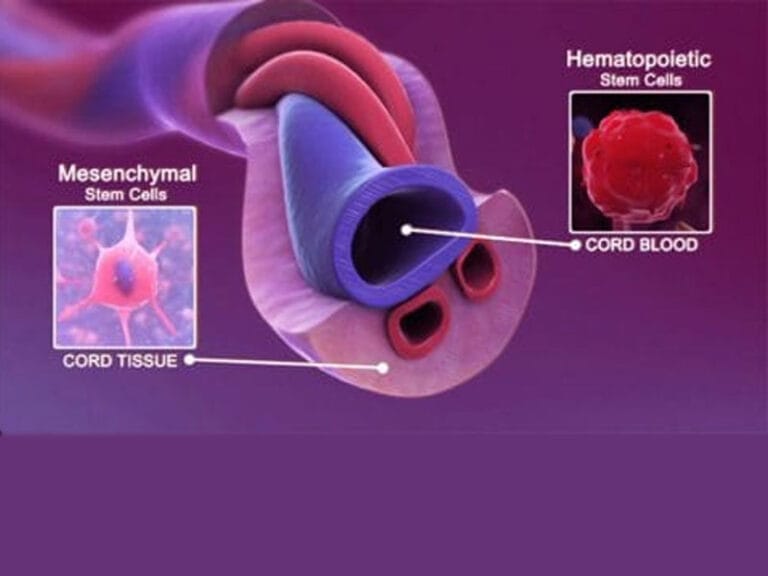
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is a cutting-edge treatment in regenerative medicine.
It involves using stem cells, which are the body’s raw materials capable of developing into various cell types, to repair and regenerate damaged tissues.
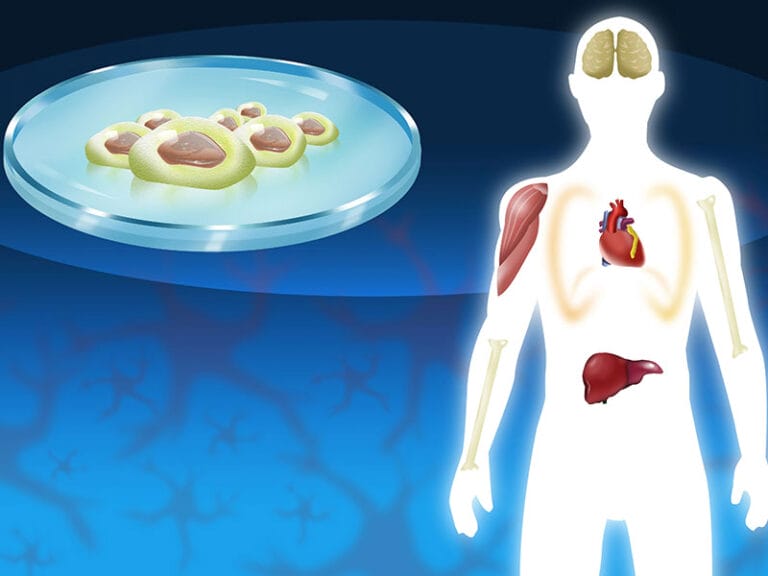
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Work for IBD?
Stem cell therapy for IBD typically involves intravenous infusion of high doses of stem cells.
These cells can:
- Respond to signals from injured tissue in the intestines.
- Reduce inflammation.
- Promote tissue repair and regeneration.
- Modulate the immune system.
The accessibility and rich blood supply of the intestines make them particularly responsive to this treatment.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy for IBD
Stem cell therapy offers several potential benefits for IBD patients:
- Improved quality of life.
- Increased energy and stamina.
- Reduced frequency and intensity of flare-ups.
- Potential to discontinue biologic infusions.
- Ability to manage health more independently.
Are You a Candidate for Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy may be an option for IBD patients who:
- Experience frequent flare-ups.
- Want to reduce dependence on medications.
- Seek to improve overall quality of life.
The Future of IBD Treatment
As research in stem cell therapy continues to advance, it holds promise as a transformative treatment for IBD.
While individual results may vary, many patients report significant improvements in their condition and quality of life following stem cell therapy.
Remember, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine if stem cell therapy is appropriate for your specific condition and circumstances.
FAQS
What is stem cell therapy and how does it work for IBD?
Stem cell therapy for IBD is a cutting-edge regenerative treatment that involves infusing high doses of stem cells intravenously to target inflammation in the digestive tract. These versatile cells work by reducing inflammation, promoting tissue repair, and modulating the immune system, potentially offering relief from IBD symptoms and improving overall gut health.
How does stem cell therapy compare to traditional IBD treatments?
Unlike traditional IBD treatments that focus on symptom management, stem cell therapy aims to address the root cause of inflammation and promote healing in the digestive tract. This innovative approach may offer advantages such as reduced dependence on medications, fewer side effects, and the potential for long-term remission, making it an attractive alternative for patients who haven’t responded well to conventional IBD treatments.
Who is a good candidate for stem cell therapy in treating IBD?
Ideal candidates for stem cell therapy in treating IBD are typically patients who have not responded well to traditional treatments or experience frequent flare-ups despite conventional management. This innovative treatment may be particularly beneficial for individuals with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who are seeking to reduce their dependence on medications, improve their quality of life, and explore a more holistic approach to managing their inflammatory bowel disease.
What are the potential benefits of stem cell therapy for IBD patients?
Stem cell therapy for IBD offers several potential benefits, including reduced inflammation, improved tissue repair, and enhanced immune system modulation in the digestive tract. Patients may experience a significant improvement in their quality of life, with reported outcomes such as decreased frequency and severity of flare-ups, increased energy levels, improved nutrient absorption, and the possibility of reducing or eliminating the need for long-term medication use in managing their inflammatory bowel disease.